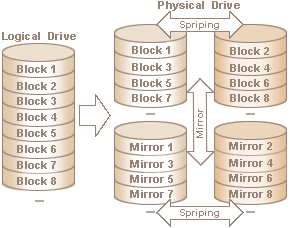
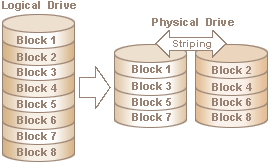
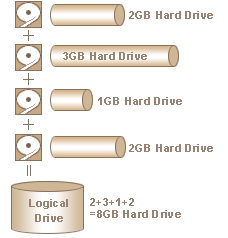
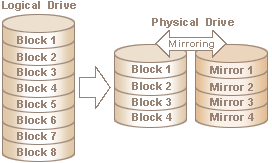
Eirp - Equivelent Isothropic Radiated power
- Equivelent Isothropic Radiated power
Transmitting (Radio) - Losses (cable,connector,arrestors) + Gains (Antennae) = 256mw
18 - 3db + 10 dbi = 256mw
3db = 2mw
6db = 4mw
9db = 8mw
18-3+10=25db
25db= 256mw approx.
DOS notes
DOS
Master Boot Record/Boot Sector – the sector where the DOS boots from. You use the switch SYS C: or format c: /s to make the MBR and the associated DOS files
Commands
DIR Directory
CD Change Directory
MD Make Directory
RD Remove Directory
DEL Delete Files
Switch- The primary command example: DIR, while
Parameter- a command that further defines the command example: /s
DIR Para.
/AH Displays hidden files only
/AS Displays system files only
/AR Displays read only files only
/B Displays files only no other info
/S Shows all files
/W Shows files in the wide format
/P Shows files page by page
/? As with any Switch gives info about switch
F3 Brings up previous command at command prompt
Right Arrow Key Reveals previous command character by character
Wild Cards *
Example dir *.com – displays .com files
Example dir *.* - displays all files
Example dir ???.* /s – shows all 3 letter files
DEL del command.com – deletes command.com
Del h*.sys – deletes system files beginning with h
*.* - deletes all files
COPY copy a:\external\*.sys c:\ – copies all .sys files in external folder
copy a:\*.com c:\ - copies all .com file to c:\ from a:\
XCOPY a:\*.* c:\ /e – copies all files and folders in the a: to the c:
COPY CON Copy Con test.txt – creates a file called test.txt
You then go o n to create the code on the subsequent lines of code
To exit and save the file press F6
TYPE Type text.txt to view that files code
Examples of .bat dir
md a:\folder1
md a:\folder2
copy a:\external\*.sys a:\folder1
del a:\folder1\*.sys
rd a:\folder1
rd a:\folder2
dir a:\*.* /s
CD \ Returns you to the Root of the drive you are on
DELLTREE deltree folder1 – removes all the files and folders contained in folder1
PATH path a:\;a:\external – maps information about a:\ and a:\external
directories
DOSKEY Command that maps executed commands allowing you to re-use
them by pressing the up and down arrow keys
config.sys device=a:\external\himem.sys – loads hi-memory
device=a:\external\ramdrive.sys e/ 2048 – creates a ramdrive of 2MB as drive E:
keyboard.exe keyb uk,, a:\external\keyboard.sys – loads the UK keyboard layout
- example line in autoexec.bat
mouse in autoexec.bat loads mouse driver
When booting press F5 to exclude the autoexec.bat and config.sys from loading, F8 will give you a step-by-step dos boot
MSCDEX The Microsoft CD-ROM DOS driver
In config.sys –
Device=a:\external\teac_cd.sys /d:name – defines the cd-rom drive
letter and name
In autoexec.bat –
a:\external\mscdex /d:name /l:r (l=drive letter)
INTER LNK device=a:\external\interlnk.exe - networking program, interlnk PC is the client; while intersrv is the server
USB use one of two drivers in config.sys
device=a:\external\aspiohci.sys or
device=a:\external\aspiuhci.sys and in autoexec you ad:
a:\external\guest.exe - it should be noted that dos will only recognize devices formatted in FAT16
y.txt/n.txt If you are writing a script any you know you are going to be faced with a y/ n query you can add a
Or you can use the y echo | to prompt the yes answer
FDISK command fdisk 1/pri:1000 - will automatically prompt fdisk to partition an active primary partition of 1000MBs
FORMAT command format c: /s - fomats and puts mbr and files onto c:
foremat c: /q - quick format
format c: /v:"" - gives volume label
Referral Use < example="">
in a batch file: format c: /v:””
ECHO y | Use this command when you have a command that automatically says yes to a
query, another example is ECHO n |, example:
echo y | format c: /v:””
SYS c: / format c: /s Both transfer the system files and make a MBR to the target disk
 Planar antennae
Planar antennae Omni directional
Omni directional Mesh antennae
Mesh antennae Omni directional 13 dbi
Omni directional 13 dbi Planer docking
Planer docking